
Podcast 23 mins
Better Being Series: Understanding Burnout in the Workplace
The European Union’s Network and Information Security (NIS2) Directive aims to ensure a “high common level of cyber security across the EU’s member states” by further strengthening current requirements. By mid-2025, the majority of the EU is expected to have adopted and published the measures necessary to meet the NIS2 regulations.
While the UK won’t implement this EU law, an expansion of the UK NIS Directive is expected to include similar requirements. UK businesses operating in the EU are encouraged to align with NIS2 standards to maintain consistent cyber security practices.
To better understand organizations’ readiness for NIS2, research was conducted amongst a group of Aon’s EMEA clients over the last year, combining elements from IT and OT assessments. The findings highlight a significant gap in NIS2 readiness, with an average score of only 58 percent across nine key cyber security measures and reporting obligations. Although areas such as authentication solutions and secure communication scored high at 79 percent, supply chain security fell significantly behind at 37 percent.
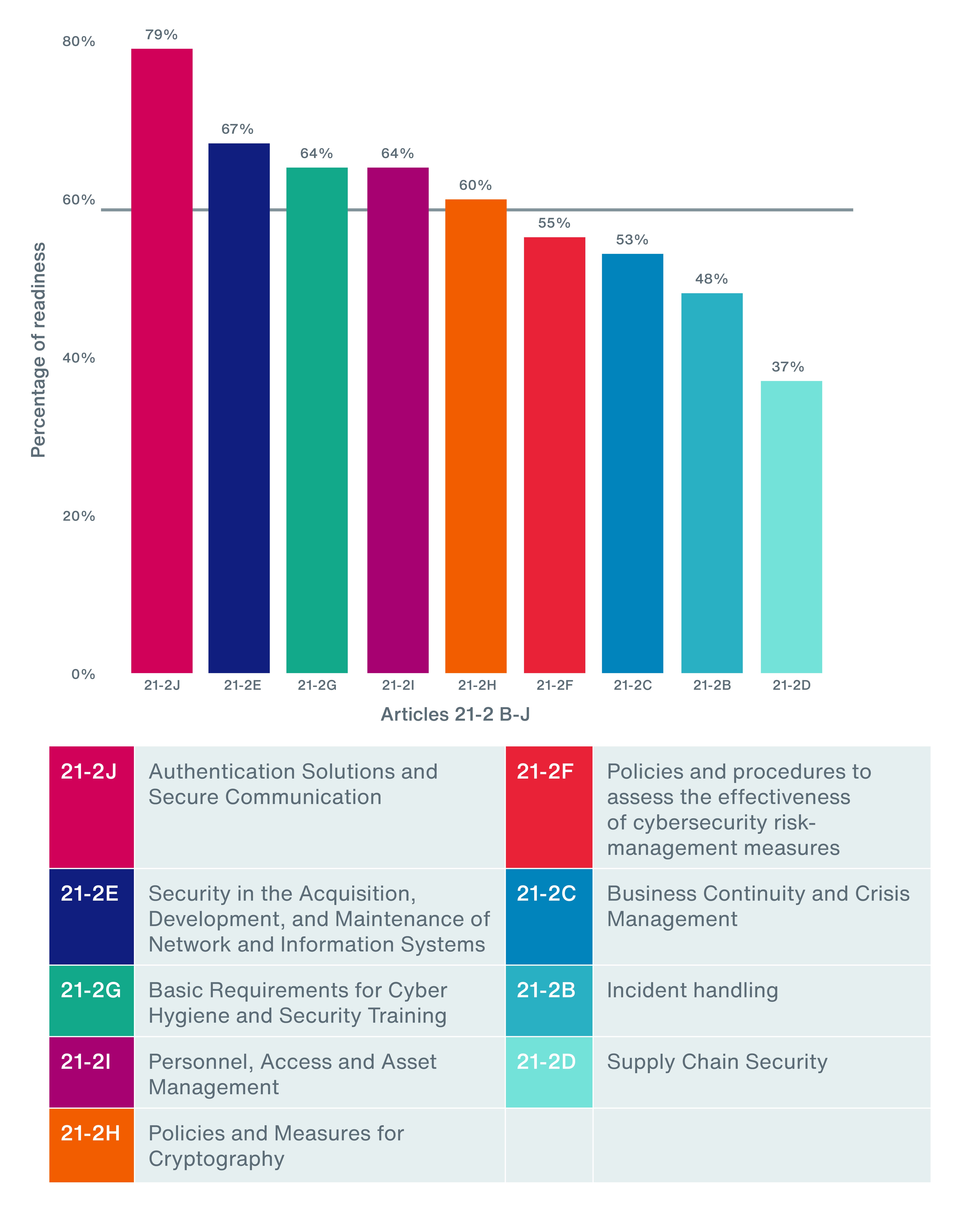
Organizations should improve their business continuity and crisis management strategies, which currently score a low 53 percent readiness, putting them in the bottom three. Most organizations have off-site backups; however, 65 percent reflect a need for better preparation for disruptions and emergencies. This finding underscores the necessity for management bodies to actively implement and regularly test business continuity plans (BCP) across IT and OT environments. While insurers have traditionally focused on examining technical controls, enhancing BCP can lead to reduced claim sizes and improved risk management.
Incident handling readiness is concerning at 48 percent. Despite 53 percent having an incident response plan (IRP), and 71 percent being aware of the need for procedures and responsibilities, there is room for improvement in conducting tabletop exercises and structuring incident handling. Management bodies must also be involved in reporting significant incidents.
The results reflect that many organizations face substantial challenges in supply chain security, with a readiness level of only 37 percent, making it the weakest area. Nearly nine out of 10 businesses examined struggle to address this vulnerability, with 88 percent finding it difficult to initiate cyber security discussions with key suppliers. Clear cyber security agreements within service-level agreements are often missing.
Management bodies must engage more actively in cyber security strategies, as they hold ultimate responsibility. Beyond business continuity and incident handling, several other control areas demand more active involvement. Management should be well-informed about specific threats to organizational assets and take responsibility for communicating cyber policy and strategy across the entire organization. Many management bodies may not fully understand the implications of cyber security and what it entails in terms of resilience. Addressing this gap is a crucial step for meeting NIS2 requirements and enhancing cyber resilience.
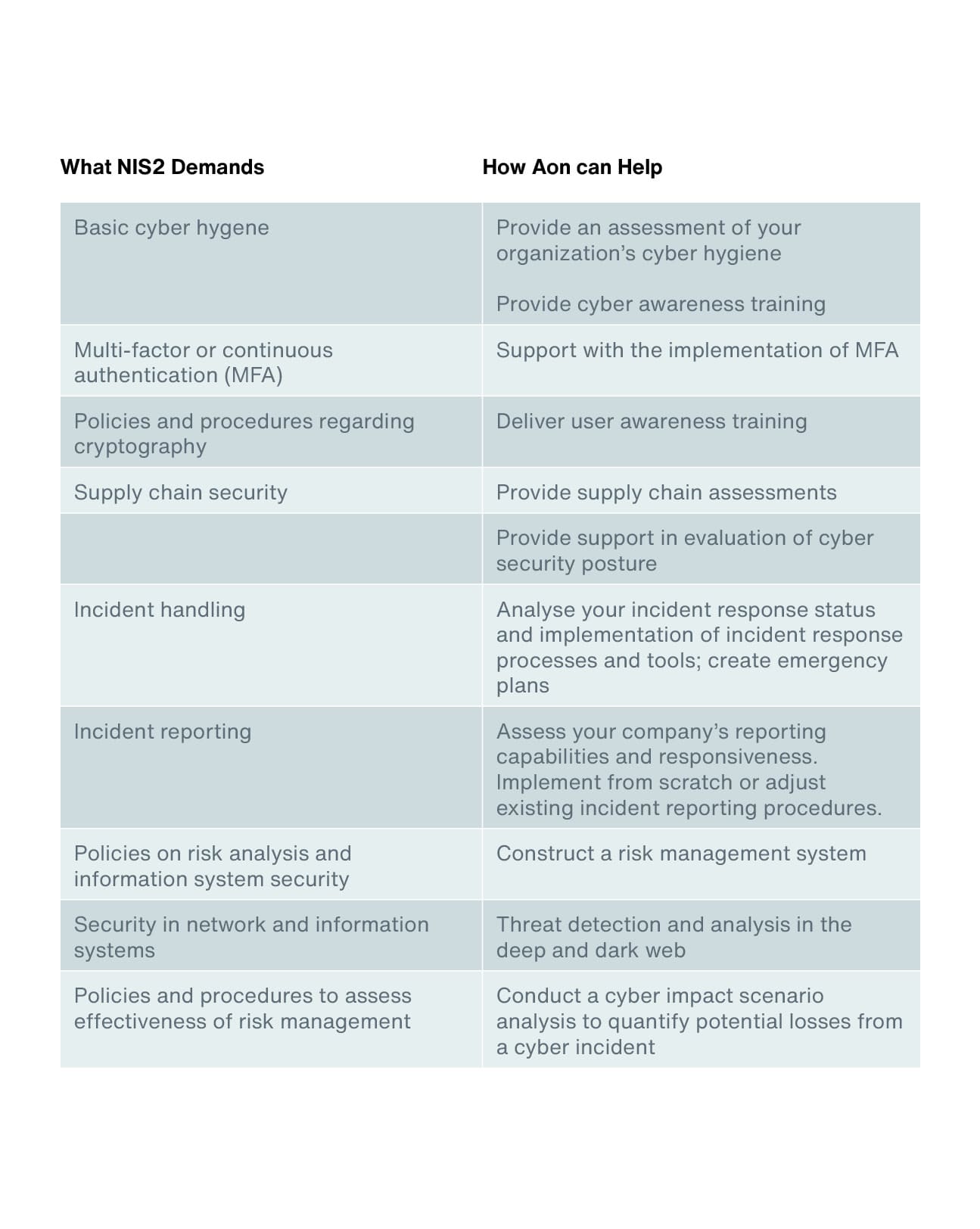
Organizations that fail to meet NIS2 requirements may face severe penalties. "Essential" companies may incur fines up to €10 million or 2 percent of total worldwide annual turnover (whichever is higher), while "important" companies face fines up to €7 million or 1.4 percent (whichever is higher).
A food production company with over €50 million in revenue faced cybersecurity gaps. Aon's initial assessment revealed urgent needs in incident response, vendor management, and vulnerability scanning. These gaps pose risks of operational disruption, impacting production and reputation, and addressing them was crucial for the company’s NIS2 compliance and resilience. Consequently, Aon conducted a full assessment and established a roadmap to help address these issues, enhancing cyber resilience and supporting the company’s compliance efforts. This helped mitigated operational risks and protected the company's reputation, in support of the Company’s goal of long-term success.
An oil industry business playing a vital role in the fuel storage and transport industry needed to comply with NIS2. While having a solid cybersecurity foundation, incident response and third-party monitoring required improvement. NIS2 compliance can help protect against cyber threats and support operational resilience and ignoring gaps can lead to disruptions and penalties. Aon conducted a risk assessment, identifying gaps and providing a roadmap that helped enhance cyber security, thereby reducing risks and potential penalties and safeguarding the company's reputation and stability.
A large food production business with over €400 million in turnover needed to boost cyber resilience to meet NIS2 requirements. Cybersecurity gaps can lead to breaches, potentially affecting operations and reputation, and addressing NIS2 requirements helps close these gaps and protect the business. Aon conducted a gap analysis and updated incident response and business continuity plans, to support compliance efforts. helping to enhance overall cyber resilience and security, supporting the company’s efforts in compliance and operational integrity.
About Cyber Solutions
Aon’s Cyber Solutions offers holistic cyber security, risk and insurance management, investigative skills, and proprietary technologies to help clients uncover and quantify cyber risks, protect critical assets, and recover from cyber incidents. Cyber security services provided by Stroz Friedberg Limited and its affiliates. Cyber risk services provided by Aon UK Limited and its affiliates. Insurance services are regulated by the FCA.
General Disclaimer
This document is not intended to address any specific situation or to provide legal, regulatory, financial, or other advice. While care has been taken in the production of this document, Aon does not warrant, represent or guarantee the accuracy, adequacy, completeness or fitness for any purpose of the document or any part of it and can accept no liability for any loss incurred in any way by any person who may rely on it. Any recipient shall be responsible for the use to which it puts this document. This document has been compiled using information available to us up to its date of publication and is subject to any qualifications made in the document.
Terms of Use
The contents herein may not be reproduced, reused, reprinted or redistributed without the expressed written consent of Aon, unless otherwise authorized by Aon. To use information contained herein, please write to our team.
Our Better Being podcast series, hosted by Aon Chief Wellbeing Officer Rachel Fellowes, explores wellbeing strategies and resilience. This season we cover human sustainability, kindness in the workplace, how to measure wellbeing, managing grief and more.
Expert Views on Today's Risk Capital and Human Capital Issues
Expert Views on Today's Risk Capital and Human Capital Issues
Expert Views on Today's Risk Capital and Human Capital Issues
Better Decisions Across Interconnected Risk and People Issues.
The construction industry is under pressure from interconnected risks and notable macroeconomic developments. Learn how your organization can benefit from construction insurance and risk management.
Our Cyber Resilience collection gives you access to Aon’s latest insights on the evolving landscape of cyber threats and risk mitigation measures. Reach out to our experts to discuss how to make the right decisions to strengthen your organization’s cyber resilience.
Our Employee Wellbeing collection gives you access to the latest insights from Aon's human capital team. You can also reach out to the team at any time for assistance with your employee wellbeing needs.
Explore Aon's latest environmental social and governance (ESG) insights.
Our Global Insurance Market Insights highlight insurance market trends across pricing, capacity, underwriting, limits, deductibles and coverages.
Better Decisions Across Interconnected Risk and People Issues.
How do the top risks on business leaders’ minds differ by region and how can these risks be mitigated? Explore the regional results to learn more.
Trade, technology, weather and workforce stability are the central forces in today’s risk landscape.
These industry-specific articles explore the top risks, their underlying drivers and the actions leaders are taking to build resilience.
Our Human Capital Analytics collection gives you access to the latest insights from Aon's human capital team. Contact us to learn how Aon’s analytics capabilities helps organizations make better workforce decisions.
Read our collection of human capital articles that explore in depth hot topics for HR and risk professionals, including using data and analytics to measure total rewards programs, how HR and finance can better partner and the impact AI will have on the workforce.
Explore our hand-picked insights for human resources professionals.
Our Workforce Collection provides access to the latest insights from Aon’s Human Capital team on topics ranging from health and benefits, retirement and talent practices. You can reach out to our team at any time to learn how we can help address emerging workforce challenges.
Our Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) collection gives you access to the latest insights from Aon's thought leaders to help dealmakers make better decisions. Explore our latest insights and reach out to the team at any time for assistance with transaction challenges and opportunities.
The challenges in adopting renewable energy are changing with technological advancements, increasing market competition and numerous financial support mechanisms. Learn how your organization can benefit from our renewables solutions.
How do businesses navigate their way through new forms of volatility and make decisions that protect and grow their organizations?
Our Parametric Insurance Collection provides ways your organization can benefit from this simple, straightforward and fast-paying risk transfer solution. Reach out to learn how we can help you make better decisions to manage your catastrophe exposures and near-term volatility.
Our Pay Transparency and Equity collection gives you access to the latest insights from Aon's human capital team on topics ranging from pay equity to diversity, equity and inclusion. Contact us to learn how we can help your organization address these issues.
Forecasters are predicting an extremely active 2024 Atlantic hurricane season. Take measures to build resilience to mitigate risk for hurricane-prone properties.
Our Technology Collection provides access to the latest insights from Aon's thought leaders on navigating the evolving risks and opportunities of technology. Reach out to the team to learn how we can help you use technology to make better decisions for the future.
Our Trade Collection gives you access to the latest insights from Aon's thought leaders on navigating the evolving risks and opportunities for international business. Reach out to our team to understand how to make better decisions around macro trends and why they matter to businesses.
Better Decisions Across Interconnected Risk and People Issues.
With a changing climate, organizations in all sectors will need to protect their people and physical assets, reduce their carbon footprint, and invest in new solutions to thrive. Our Weather Collection provides you with critical insights to be prepared.
Our Workforce Resilience collection gives you access to the latest insights from Aon's Human Capital team. You can reach out to the team at any time for questions about how we can assess gaps and help build a more resilience workforce.

Article 6 mins
Addressing the retirement pay gap issue between men and women starts with first acknowledging it exists. Then companies can conduct further analysis and adjust their benefit plans accordingly.

Article 8 mins
AI acceleration, rising healthcare costs and changes to workforce skills are transforming organizations. Our analysis of financial services, life sciences and technology companies provides insights on how to redesign roles, reskill at scale and reimagine talent strategies to stay competitive.

Article 10 mins
Workforce-related risks — spanning health, benefits, safety systems, and data and analytics — are not just operational concerns but strategic drivers. When activated, they positively shape the total cost of risk and long-term resilience for industrials and manufacturing organizations.