Drivers of Captive Growth and Market Stabilization
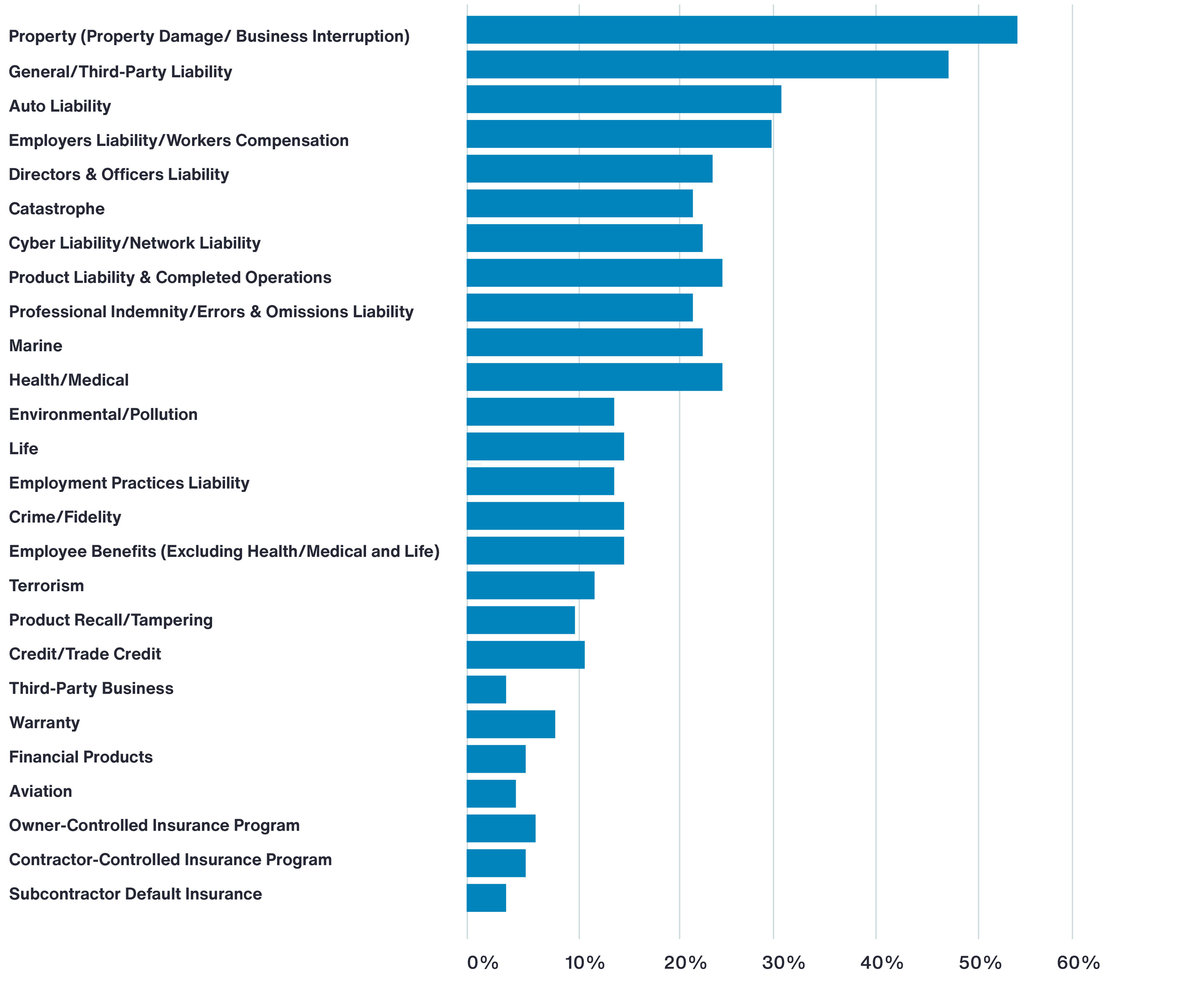
A combination of market dynamics and organizational capabilities is propelling captive adoption. Historically, challenging conditions in the insurance market drove companies toward alternatives like captives. For cyber specifically, recent softening has made traditional placements more accessible in the near term — but that’s only part of the picture.
Advances in data, modeling and analytics are enabling sharper insight into cyber exposure, increasing confidence to retain risk through captives and other innovative structures. Captives are also providing a route to reinsurance markets — where underwriting can be more flexible — and, in some regions, regulatory shifts have simplified set-up and operation.
The recent stabilization — or slight decline — in captive usage since 2023 should not be read as a reversal. Rather, it may reflect a temporary period of increased competition and capacity in cyber.